Current Nutrition Strategies in the Prevention and Management of Diabetes Mellitus
Keywords:
Diabetes Mellitus, nutrition strategies, personalized nutrition, blood glucose control, weight management, lipid profile, individualized approachesAbstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) continues to be a significant global health challenge, requiring a comprehensive approach to its prevention and management. This study explores recent developments in customized nutritional strategies to address the complexities of DM. The study utilized an observational and experimental design, involving individuals diagnosed with DM. Data collection included health and nutrition surveys, laboratory analyses, and individualized nutrition interventions. Results showed substantial improvements in fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels, weight loss, and improved lipid profiles following the personalized nutrition intervention. The discussion emphasizes the effectiveness of personalized nutrition strategies, stressing the importance of an individualized approach and highlighting the positive impact on blood glucose control, weight management, and lipid profiles. The findings show promising implications for clinical practice, emphasizing the potential for developing more effective and individualized nutritional guidelines for the prevention and management of Diabetes Mellitus. Limitations and avenues for further research are discussed, emphasizing the need for a larger sample size and longer follow-up period. In conclusion, this study contributes valuable insights into the role of current nutritional strategies in the holistic management of Diabetes Mellitus, paving the way for improved personalized care and better outcomes.
Downloads
References
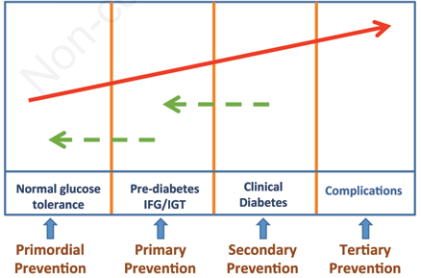
Bhattacharya, Prasanta K., and Aakash Roy. "Primary prevention of diabetes mellitus: current strategies and future trends." Italian Journal of Medicine 11.1 (2017): 15-22.
Pegklidou, Kyriaki, Ioannis Nicolaou, and Vassilis J Demopoulos. "Nutritional overview on the management of type 2 diabetes and the prevention of its complications." Current diabetes reviews 6.6 (2010): 400-409.
Asosiasi Diabetes Amerika. (2022). Standar Perawatan Medis pada Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care, 45(Supplement_1), S1-S225. [DOI: 10.2337/dc22-SINT]
Franz, M. J., MacLeod, J., Evert, A., Brown, C., & Gradwell, E. (2015). Akademi Nutrisi dan Diet Pedoman Praktik Nutrisi untuk Diabetes Tipe 1 dan Tipe 2 pada Orang Dewasa: Tinjauan Sistematis Bukti Efektivitas Terapi Gizi Medis dan Rekomendasi untuk Integrasi ke dalam Proses Perawatan Gizi. Jurnal Akademi Nutrisi dan Dietetika, 115(11), 1656-1669. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jand.2015.08.012]
Bolla, AM, Caretto, A., Laurenzi, A., Scavini, M., & Piemonti, L. (2019). Diet Rendah Karbohidrat dan Ketogenik pada Diabetes Tipe 1 dan Tipe 2. Nutrients, 11(5), 962. [DOI: 10.3390/nu11050962]
Dyson, PA, Twenefour, D., Breen, C., Duncan, A., Elvin, E., Goff, L., ... & Walden, E. (2018). Pedoman nutrisi berbasis bukti Diabetes UK untuk pencegahan dan pengelolaan diabetes. Diabetic Medicine, 35(5), 541-547. [DOI: 10.1111/dme.13603]
Evert, A. B., Dennison, M., Gardner, C. D., Garvey, W. T., Lau, K. H. K., MacLeod, J., ... & Rewers, M. (2019). Terapi nutrisi untuk orang dewasa dengan diabetes atau pradiabetes: Sebuah laporan konsensus. Diabetes Care, 42(5), 731-754. [DOI: 10.2337/dci19-0014]